Improving your SEO takes a lot of time and energy. Not to mention an understanding of how search engines crawl and read your website. Back in the summer of 2011, Bing, Google, Yahoo!, and Yandex gave us a gift—a path to improve our Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) through Schema markup. All of these search engines worked together to launch Schema.org and create a common set of tags that make notating HTML much easier so that search engine robots can understand the content on your website. In this post, we’ll discuss what Schema is, what Schema isn’t, how it impacts your approach to SEO, and some tools to help you start marking up your website properly.
What is Schema markup?
Schema markup is a collection of HTML tags that allows search engine robots to interpret the type of content on your site. These tags help search engines return more informative and relevant results for users. The full list of tags that are used in Schema markup can be found on Schema.org.
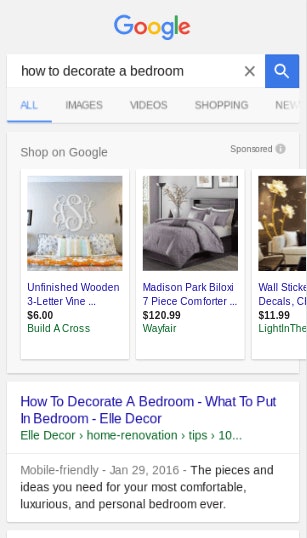
So how does this work? For example, let’s say I write a blog about a salsa recipe. The search engine will crawl this blog, and produce a search engine result about a salsa recipe. However, if the correct schema markup is used within the article, search engine results can also display an image, user ratings, prep/cook time, the calorie count of the salsa recipe, and more. By properly marking up my salsa recipe, I’ve enabling the search engines to display a wide array of relevant information to the user.
What is the difference between Microdata, Schema and structured data?
If you’re starting your journey into schema markup, you have probably heard of other terms like “microdata” and “structured data,” so you might be confused about how those terms relate.
Structured data is defined by Yoast SEO as “…code in a specific format, written in such a way that search engines understand it. Search engines read the code and use it to display search results in a specific and much richer way. You can easily put this piece of code on your website.” Interestingly enough, schema markup is a form of “structured data” that is agreed upon by search engines. It is also known as “structured data mark up,” and “Microdata” is the HTML5 specification for structured data. Other structured data formats supported by Google are microformats and RDFa, but Microdata is the format that’s preferred by Google. To learn more about structured data from Google, read this article.
Types of items described by Schema
Schema can be used to mark up all kinds of items from products to events to salsa recipes. It is used to give further information on:
- Events
- Places of Business/Organizations
- Locations
- Products
- Noteworthy People
Types to mark up
Rich search results: expanded content and details that help users quickly get information about the keyword they searched.
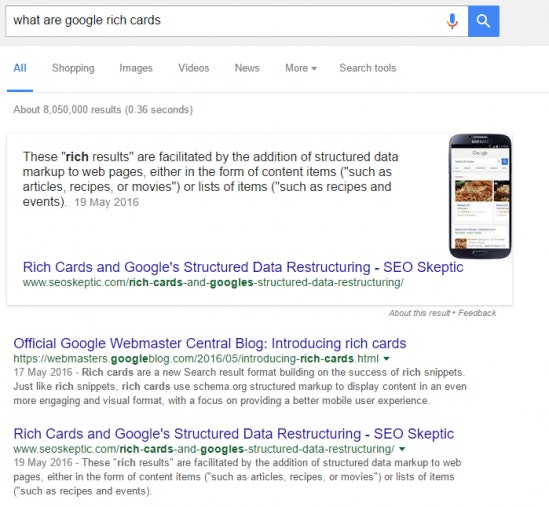
Rich cards: A different style of rich search results in the form of cards, designed for mobile.
Knowledge Graph: Often a group of sources that appear in images across the top of the page.
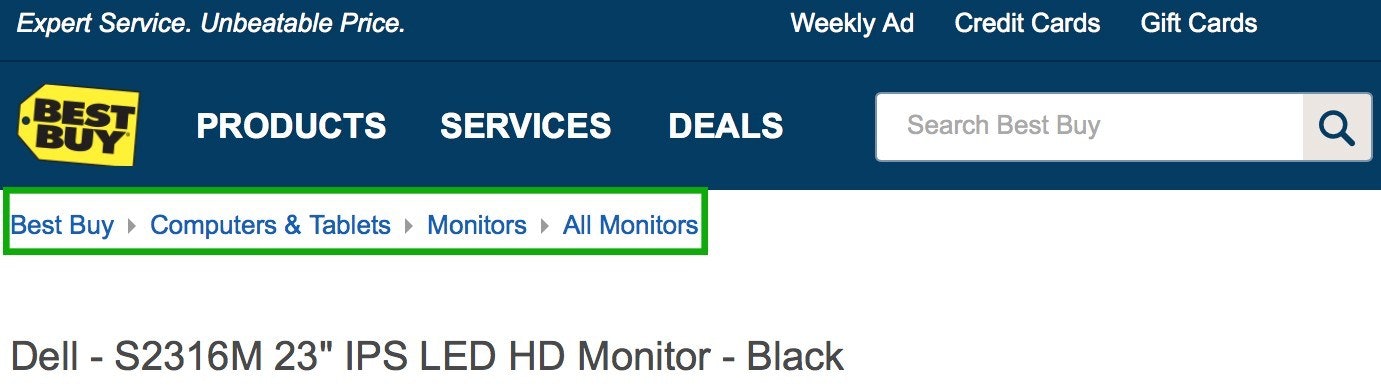
Breadcrumbs: A breadcrumb trail is a small text section (occasionally necessary for websites with a complicated structure or a variety of pages).
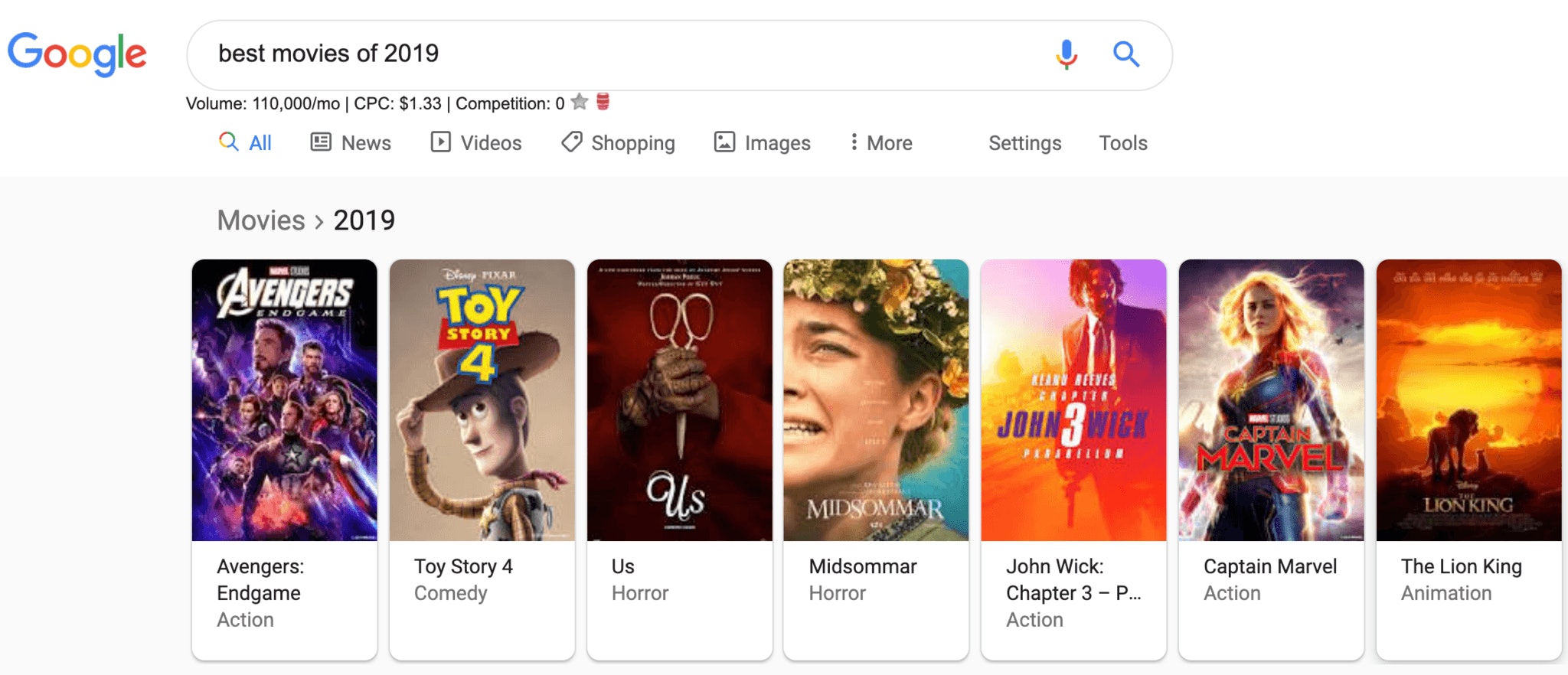
Carousels: Rich results in a carousel style, designed for mobile but used in desktop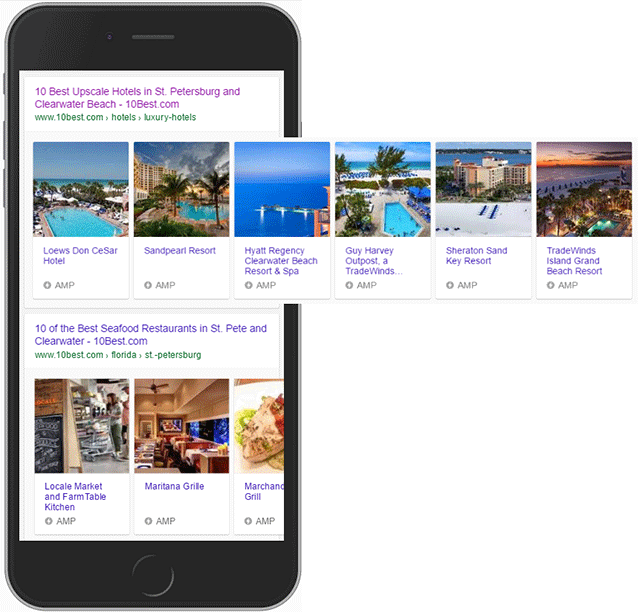
How Schema impacts your SEO
Adding Schema markup to your HTML improves your appearance in search results and the way your page displays by enhancing what displays from your website content. It also improves your click-through rate (CTR) and drives additional traffic because it’s more visually appealing, provides additional information to searchers, and acts as a strong user signal.
Improves Local SEO
Marking up your web pages for your business will allow your business to properly show up in search engines. Tools like Google My Business and Bing Places support local business with intuitive interfaces that allow you to update your company information. These tools help you and your business manage how your information appears in search engines.
User first
Search engines over the years have gradually placed a greater emphasis on user experience. The easier it is for users to find information on your site and interact positively, the better. If you can mark up your site properly in visually appealing ways with things like rich snippets and carousels, it will help the users who are searching for you find the information they need. This information also helps your website rank better and, in turn, get more clicks.
Avoid spam
Pro tip: Mark up pages accurately.
Think about user intent when you’re implementing Schema for that page. For example, don’t mark up a page about an author with markup that is intended for writing a salsa recipe. That might be an extreme example, but when pages are improperly using Schema markup for multiple pages, your website can be flagged as spammy – with a resulting decline in rankings.
Tools to use for Schema
Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool
Basic structured data tool from Google. Enter your URL or a piece of code, then run the test to see what elements are displaying and diagnose problems instantly.
SEO SiteCheckup’s Microdata Schema Test
This tool is different from others because it allows you to compare your site’s markup to another competitor. It’s as easy as inputting your URL and your competitors to get started.
Follow the breadcrumbs to better results.
Schema markup is an SEO innovation that’s not going away anytime soon. I encourage you to learn how to implement Schema to your website and mark up relevant microdata to improve your search results. Doing so right away will give you a clear competitive advantage.